IPFS
IPFS is a peer-to-peer (p2p) content storage and retrieval system. It utilizes content addressing (identifying content by what it is) rather than location addressing (identifying content by where it is) to organize files on its network.
The Geo Web utilizes IPFS as the basis for its open, censorship resistant, resilient, and efficient content layer. Linked media on the Geo Web are essentially geo-anchored IPFS files.\
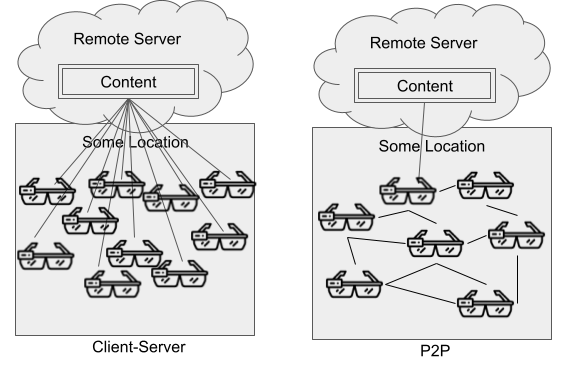
Geo Web users seeking the same content will for the most part be geographically clustered. This is an optimal environment for p2p transmission: reduced search radius for peers, shorter transmission distance, and network redundancy. As media on the Geo Web grows in volume and fidelity (especially with augmented reality), leveraging p2p transmission could significantly improve performance and network scalability.
Users can trust the authenticity of a requested file on IPFS regardless of who it is served by because every file gets a unique content identifier (CID) generated through a cryptographic hashing algorithm. Identical files will always produce identical CIDs when run through a hashing function. But, changing just one pixel (or, more dramatically, trying to insert anything malicious) in a file will always result in a completely different CID. A CID is easily verified and can’t be faked, so a file identified with a CID is always what it says it is.
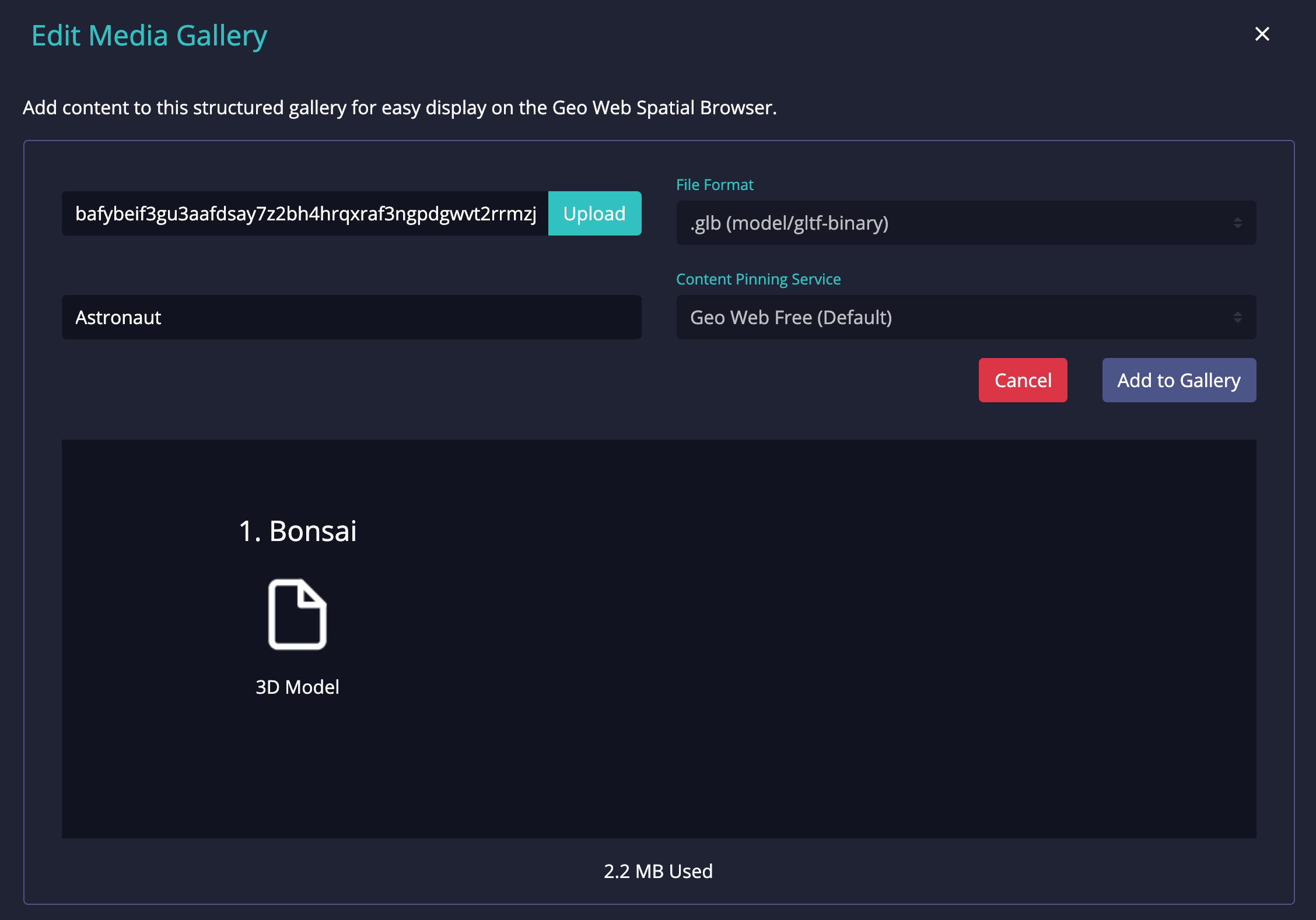
The Cadastre's current publishing tools enable uploads digital content to the IPFS network via a IPFS node running in the browser. Uploaded content is hashed to produce its CID then pinned and archived via a 3rd-party service to provide persistence on the IPFS network.
---
Check out IPFS's official documentation to learn more.